Chemical Imbalance in the Brain: Myth or Reality?
Have you ever heard someone say they have a “chemical imbalance” in their brain? Or maybe you’ve read it in an article or watched a documentary about mental health. The term is often tossed around, but what does it mean? Is “chemical imbalance in the brain” a real medical condition, or is it just a myth? Today, let’s dive into this topic and uncover the truth behind one of the most talked-about aspects of mental health.
What is a Chemical Imbalance in the Brain?
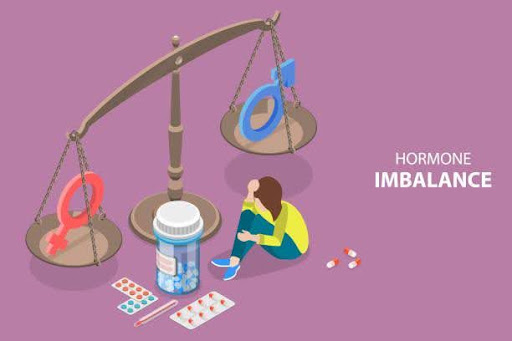
First off, when we talk about a chemical imbalance in the brain, we’re referring to disruptions in the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help transmit signals between nerve cells, allowing different parts of the brain to communicate with each other. Examples of neurotransmitters include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). These brain chemicals play a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and overall brain function.
If the levels of these neurotransmitters are too high or too low, it can lead to a range of mental health problems. For example, low serotonin levels are often linked to depression, while dopamine imbalances may contribute to conditions like schizophrenia or addiction. This imbalance in chemical levels is sometimes cited as the cause of many mental health disorders.
But, here’s where it gets tricky: while the idea of a chemical imbalance is popular in the world of psychiatry, it isn’t universally agreed upon by all scientists. So, let’s break it down and see whether it’s a solid scientific fact or just a myth.
Common Symptoms of Chemical Imbalance in the Brain
A chemical imbalance in the brain can manifest in various ways, depending on which neurotransmitter is affected and the severity of the imbalance. Here are some common symptoms to watch out for:
1. Mood Swings and Irritability
Mood swings can be a classic sign of a chemical imbalance, particularly if you’re feeling happy one minute and suddenly irritable or anxious the next. Low serotonin levels are often linked to mood disorders like depression and anxiety, while dopamine imbalances can cause emotional instability.
2. Depression and Persistent Sadness
Low serotonin levels are one of the most common suspects behind depression. When serotonin levels are out of balance, it can cause feelings of hopelessness, deep sadness, and a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed. This imbalance can affect your energy levels, concentration, and ability to sleep.
3. Anxiety and Panic Attacks
Anxiety can also be linked to imbalances in neurotransmitters. Low levels of serotonin, for instance, are associated with heightened feelings of fear or nervousness. If you find yourself frequently experiencing panic attacks, sweating, rapid heartbeat, or trouble breathing, it might be related to a chemical imbalance in your brain.
4. Sleep Disorders
Your sleep patterns are heavily influenced by the balance of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin and melatonin. A chemical imbalance could cause either insomnia (difficulty sleeping) or hypersomnia (sleeping too much), leaving you feeling exhausted even after a full night’s rest.
5. Lack of Focus and Motivation
Dopamine plays a key role in motivation, attention, and focus. When dopamine levels are too low, you may feel unmotivated, sluggish, or unable to concentrate on tasks. This is often seen in conditions like ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder), but it can also occur in people who are dealing with stress or depression.
6. Changes in Appetite
If you notice significant changes in your appetite—either eating too much or losing your appetite entirely—it could be a sign of an imbalance in your brain’s chemical systems. For instance, serotonin imbalance may lead to overeating or a lack of interest in food. On the other hand, dopamine imbalance can affect your craving for pleasure and satisfaction, potentially leading to overeating or eating disorders.
7. Hallucinations and Delusions
When dopamine is significantly imbalanced, it can lead to more severe symptoms like hallucinations, delusions, or paranoia. These are often seen in psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
Is a Chemical Imbalance Really the Cause?
Now, here’s where things get a bit more complicated. While the concept of a chemical imbalance in the brain has been widely used in both clinical settings and the media, some experts argue that it’s an oversimplification of the actual causes behind mental health disorders.
The “chemical imbalance” theory is based on the idea that mental illnesses like depression or anxiety are caused by an imbalance in neurotransmitter levels. However, this theory does not consider the full range of biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to mental health conditions.
For example, many factors can affect neurotransmitter levels, including genetics, trauma, chronic stress, diet, and even gut health. This suggests that while a chemical imbalance may be one piece of the puzzle, it’s not necessarily the sole cause of mental health conditions.
Moreover, treatments like antidepressant medications (which aim to correct chemical imbalances) work for some people but not for everyone, suggesting that the role of neurotransmitters in mental illness is still a topic of ongoing research.
The Role of Medication and Therapy
Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and dopamine agonists are commonly prescribed to help “rebalance” neurotransmitters in the brain. These medications can help alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues, but they are not a cure-all. In many cases, therapy—particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)—is used in conjunction with medication to address the root causes of mental health conditions, like negative thought patterns or unresolved trauma.
While medications can help manage symptoms, they may not necessarily fix the underlying causes of a chemical imbalance. This is why an integrated approach, combining both medication and therapy, is often considered the most effective way to treat mental health conditions.
FAQs about Chemical Imbalance in the Brain
Q1: Can a chemical imbalance cause depression? Yes, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin are often linked to depression. However, depression can also be caused by a range of other factors, including genetics, environmental stressors, and psychological factors.
Q2: How do I know if I have a chemical imbalance? If you’re experiencing symptoms like mood swings, sleep problems, anxiety, or depression, it’s important to consult a mental health professional for an accurate diagnosis. They can assess your symptoms and recommend treatment options.
Q3: Can therapy help with a chemical imbalance in the brain? Yes, therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help you address the root causes of emotional distress and manage the effects of a chemical imbalance. Therapy may also be combined with medication for a more holistic treatment approach.
Q4: Are antidepressants the only way to treat a chemical imbalance? No, antidepressants are one option, but they may not be effective for everyone. Lifestyle changes, therapy, stress management techniques, and a healthy diet can also help support a healthy brain chemistry.
Q5: Is chemical imbalance in the brain a permanent condition? Not necessarily. Chemical imbalances may fluctuate over time due to various factors, including stress, life events, or changes in medication. With the right treatment and support, many people can manage their symptoms effectively.
Conclusion: Chemical Imbalance in the Brain – Fact or Fiction?
So, is the idea of a chemical imbalance in the brain a myth or a reality? The truth is, it’s a bit of both. While there is evidence suggesting that imbalances in neurotransmitters play a role in mental health conditions, it’s also clear that mental health is influenced by a complex web of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Ultimately, understanding and managing a chemical imbalance in the brain requires a comprehensive approach that considers not just medication, but therapy, lifestyle changes, and support systems. If you suspect you’re dealing with a chemical imbalance, seeking professional help is the first step toward reclaiming your mental well-being.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Hip Hop Hip Hop!